Dementia is a complex and often misunderstood condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. In this blog, we’ll delve into the myths and facts surrounding dementia, examine its causes and symptoms, and explore potential solutions for managing and supporting individuals living with this condition. By shedding light on dementia and fostering greater understanding, we can work towards a more compassionate and supportive society for those affected by this challenging condition.

Myths and Facts
Myth: Dementia is a normal part of aging.
Fact: While dementia is more common in older adults, it is not a normal part of the aging process. Dementia is a neurodegenerative condition characterized by a decline in cognitive function that interferes with daily life.
Myth: Memory loss is the only symptom of dementia.
Fact: While memory loss is a common symptom of dementia, it is not the only indicator. Dementia can also manifest as difficulties with language, executive function, problem-solving, and changes in mood or behavior.
Myth: Dementia is untreatable and irreversible.
Fact: While there is currently no cure for dementia, early diagnosis and appropriate management strategies can help slow the progression of the condition and improve quality of life. Treatment options may include medication, lifestyle modifications, and supportive therapies.

Causes of Dementia
Dementia can be caused by various underlying conditions and factors, including:
Alzheimer’s disease: The most common cause of dementia, characterized by the accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain.
Vascular dementia: Caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, often due to stroke or small vessel disease.
Lewy body dementia: Characterized by the presence of abnormal protein deposits in the brain, leading to cognitive and motor symptoms similar to Parkinson’s disease.
Frontotemporal dementia: A group of disorders characterized by progressive damage to the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, leading to changes in behavior, personality, and language.

Symptoms of Dementia
Dementia is a progressive condition characterized by a decline in cognitive function that interferes with daily life. While the specific symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause and the areas of the brain affected, common manifestations of dementia include:
Memory Loss – Memory loss is often one of the earliest and most noticeable symptoms of dementia. Individuals may have difficulty remembering recent events, appointments, or conversations. They may repeatedly ask the same questions or rely heavily on memory aids such as notes or calendars.
Difficulty with Language – Dementia can impact language abilities, making it challenging for individuals to find the right words, follow conversations, or express themselves clearly. They may struggle to name familiar objects or people and may rely on vague or nonspecific language.
Impaired Judgment and Reasoning – Dementia can affect an individual’s ability to make sound judgments and decisions. They may have difficulty assessing risks, understanding consequences, or solving problems. This can lead to poor decision-making in everyday situations, such as financial matters or personal safety.
Changes in Mood or Behavior – Dementia can cause changes in mood, personality, and behavior. Individuals may experience shifts in mood, ranging from apathy and depression to irritability and agitation. They may also exhibit socially inappropriate behaviors, impulsivity, or lack of inhibition.
Disorientation and Confusion – Disorientation and confusion are common symptoms of dementia, particularly in later stages of the disease. Individuals may become lost in familiar surroundings, lose track of time, or have difficulty recognizing people they know well. They may also experience difficulty understanding their current location or situation.
Difficulty with Motor Skills – Dementia can impact motor skills and coordination, leading to difficulties with tasks such as dressing, grooming, or eating. Individuals may experience tremors, stiffness, or clumsiness, making it challenging to perform activities of daily living independently.
Hallucinations or Delusions – In some cases, individuals with dementia may experience hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that aren’t there) or delusions (false beliefs or perceptions). These symptoms can be distressing for both the individual and their caregivers and may require careful management and support.

Solutions for Dementia
While there is currently no cure for dementia, there are various strategies and interventions that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals living with the condition. In addition to traditional approaches, emerging therapies and technologies show promise in supporting cognitive function and overall well-being:
Medication – Certain medications may help alleviate symptoms of dementia, such as cognitive enhancers for Alzheimer’s disease or antidepressants for mood disturbances. While these medications do not halt the progression of the disease, they can temporarily improve cognitive function and quality of life for some individuals.
Lifestyle Modifications – Healthy lifestyle choices play a crucial role in supporting brain health and overall well-being for individuals with dementia. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, adequate sleep, and social engagement can help maintain cognitive function and delay the progression of the disease.
Cognitive Stimulation – Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, such as puzzles, games, and hobbies, can help maintain cognitive function and slow the progression of dementia. Cognitive stimulation programs, including memory exercises, problem-solving tasks, and creative activities, offer opportunities for socialization and cognitive enrichment.
Supportive Therapies – Occupational therapy, speech therapy, and physical therapy can help individuals with dementia maintain independence and function in daily activities. These supportive therapies focus on maximizing functional abilities, improving communication skills, and enhancing mobility and coordination.
Neurofeedback – Neurofeedback therapy involves training individuals to regulate their brainwave activity through real-time feedback provided by electroencephalography (EEG) sensors. This non-invasive technique aims to improve cognitive function, attention, and emotional regulation in individuals with dementia by promoting neural plasticity and reorganizing brain networks.
Photobiomodulation (PBM) – PBM therapy utilizes light energy to stimulate cellular function and promote healing in the brain. Research suggests that PBM may have neuroprotective effects and improve cognitive function in individuals with dementia by reducing inflammation, enhancing mitochondrial function, and promoting neurogenesis.
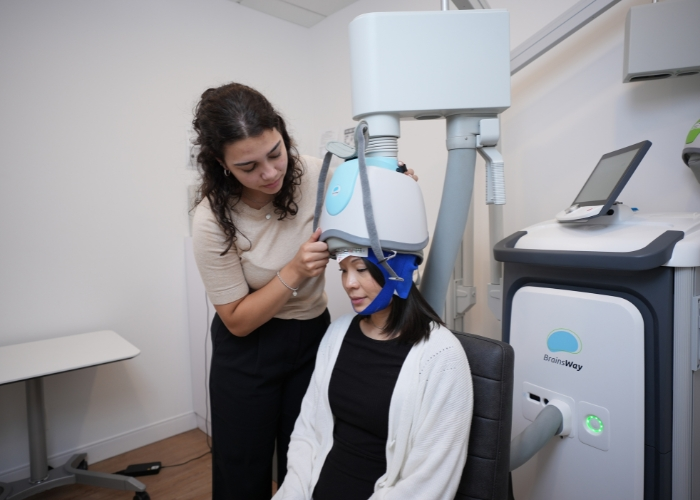
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) – TMS is a non-invasive brain stimulation technique that uses magnetic fields to modulate neural activity in targeted regions of the brain. While still in the early stages of research for dementia, TMS shows potential as a therapeutic intervention for improving cognitive function and reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety in individuals with dementia.
Biofeedback – Biofeedback techniques can help individuals with dementia learn to control physiological responses to stress and improve self-regulation. By providing real-time feedback on physiological parameters such as heart rate variability, skin conductance, and muscle tension, biofeedback promotes relaxation, stress reduction, and emotional well-being.
Incorporating a combination of traditional approaches and emerging therapies, individuals with dementia can access comprehensive and personalized care that addresses their unique needs and promotes optimal quality of life. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual preferences, medical history, and stage of the disease.
Conclusion
Dementia is a complex and challenging condition that affects individuals and families worldwide. By dispelling myths, understanding the causes and symptoms, and exploring potential solutions, we can work towards a more compassionate and supportive society for those affected by dementia. Through early diagnosis, appropriate management strategies, and a holistic approach to care, we can improve the quality of life for individuals living with dementia and support them on their journey toward dignity and well-being.
Elumind Centres for Brain Excellence is an integrated mental health centre offering solutions that can help you with your mental/brain health needs. To start your journey, book your FREE 15-MINUTE PHONE CONSULTATION. We are here for you.








